Patchy distribution of joint inflammation in arthritis resolved
VIB | 11-15-2018
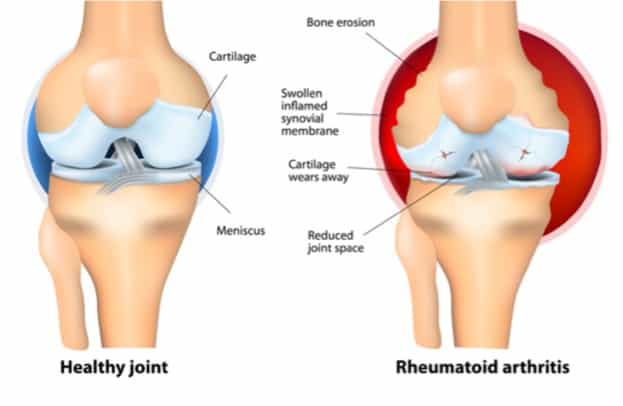
Chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and spondylo-arthritis (SpA) are chronic disabling diseases that have a poor outcome on loco-motoric function, if left untreated. RA en SpA affect each about 1% of the population. The reason why certain joints are more affected than others has been a longstanding question, resolved by Isabelle Cambré and Prof. Dirk Elewaut from the VIB-UGent Center for Inflammation Research who published their results in Nature Communications.
They found that biomechanical forces are key drivers behind this observation. By studying the inflammation induced bone erosions in detail they identified certain hot spots in the musculoskeletal system where joint inflammation and erosions are more likely to occur. These sites are especially sensitive to mechanical loading and explain the clinical pattern of joint involvement described in human patients.
The team also discovered the underlying mechanisms, which involves release of certain inflammatory mediators, like chemokines, by joint resident cells in response to mechanical stress. This in turn leads to recruitment of certain white blood subsets, classical monocytes, into mechanically stressed regions where they mediate inflammation and subsequently tissue damage such as erosions.
Isabelle Cambré (VIB-UGent): “Our results explain to a large degree the patchy nature of joint inflammation in human arthritis and the clinical pattern of joint involvement.” We are currently trying to unravel the underlying pathways driving this inflammation: we are excited about this as this is potentially a new area of research at the intersection of mechanobiology and inflammation.
Source:
Materials provided by VIB (The Flanders Institute for Biotechnology). Content may be edited for clarity, style, and length.
